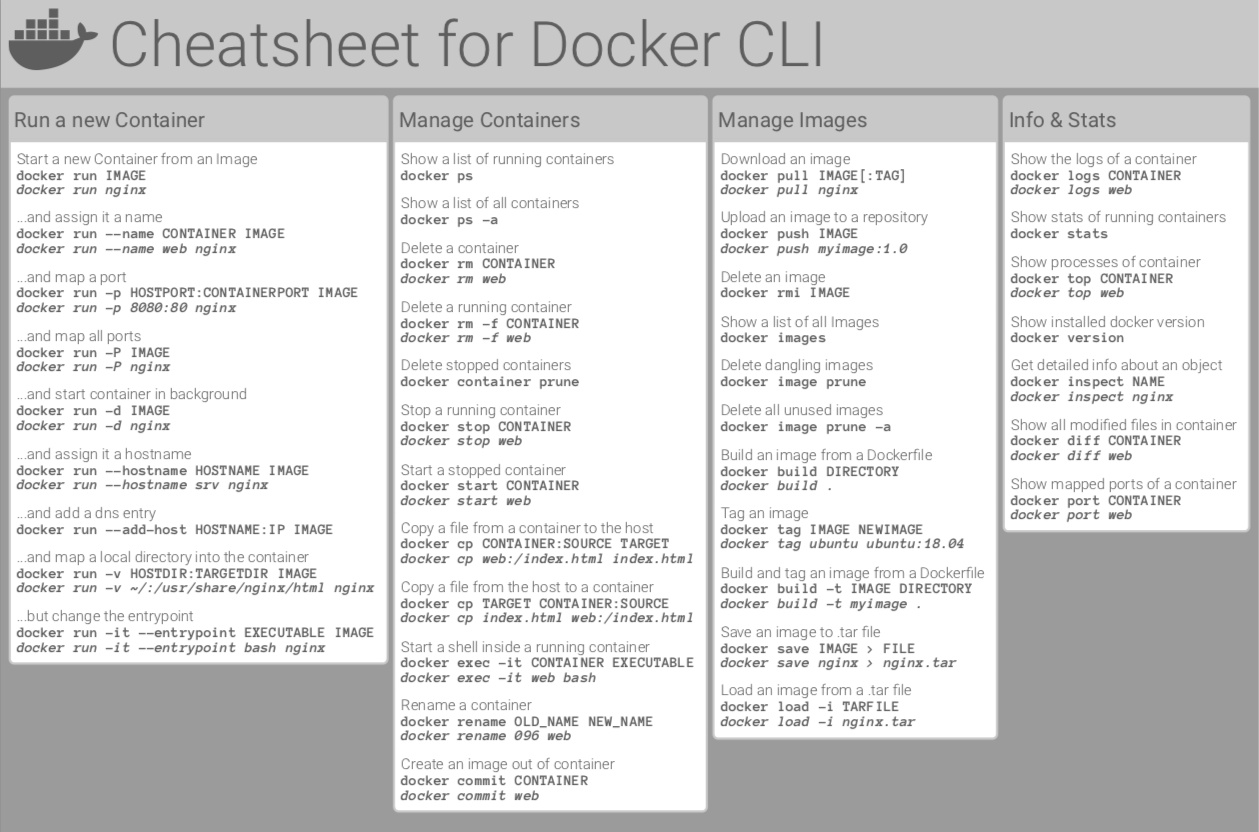
- Docker Cli Commands Cheat Sheet Printable
- List Of Docker Commands
- Docker Command Reference
- Docker Cli Commands Cheat Sheet
- Docker Cheat Sheet Pdf
- Docker Cheat Sheet 2020
- Docker Kubernetes Service Cheat Sheet Docker Desktop Run Docker Kubernetes Service includes Compose on Kubernetes by default for both UCP clusters and Desktop.
- Docker is fantastic tool for building out your infrastructure, however it does have a fairly steep learning curve. That’s why I created this Docker Cheat Sheet.I was constantly looking up what docker commands I needed to run to build an image from a dockerfile, run a container, mount a volume, etc.
Early post Docker for beginners ,we talked about how to start with dockers
Here are few basic commands which we need on daily base work case with docker
Useful Docker Commands helpful for operation
Run commands in a container. Docker start docker start options CONTAINER -a, -attach # attach stdout/err -i, -interactive # attach stdin docker stop options CONTAINER Start/stop a container. Docker ps $ docker ps $ docker ps -a $ docker kill $ID Manage containers using ps/kill. The one-page guide to Docker CLI: usage, examples, links, snippets, and more.
1) To Build Docker image from Dockerfile
# docker build -t thegeeklinux:1.0 .
-t for Image name and tag name:tag (If you will not give tag it will tag latest)
2) To list images : # docker images
3) To save docker image in tar file : # docker save -o /tmp/thegeeklinux.tar thegeeklinux:1.0
4) To delete docker image : # docker rmi -f thegeeklinux:1.0
-f forcefully
5) To load docker image from tarball : # docker load < /tmp/thegeeklinux.tar
6) To tag docker image : # docker tag thegeeklinux:1.0 localhost:5000/thegeeklinux:1.0
NOTE:localhost:5000 should be your private registry ip and port
7) To push image to private or public registry server # docker push localhost:5000/thegeeklinux:1.0
NOTE: replace localhost with your private registry hostname or ip.
8) To pull docker image for private or public registry
a) To pull image from private registry server # docker pull localhost:5000/thegeeklinux:1.0
NOTE :replace localhost with your private registry hostname or ip.
b) To pull image from public registry # docker pull ubuntu
Docker Container Operation
1) To RUN Docker container : # docker run -it thegeeklinux:1.0
-i interactive mode
-t attract terminal
# docker run -d --name thegeeklinux -p 80:80 -h tgl -l 'com.thegeeklinux=1.0' -e WORKDIR=/opt/thegeeklinux thegeeklinux:1.0
-d Detach it will run container in backgraund.
-e set environment for container
-h Hostname you can give hostname to container also
-l we can give label also to container for indentification.
-p we can open port to host from container
–name Name of the container
2) To Run command inside docker container # docker exec thegeeklinux ls
3) Login to container without ssh : # docker exec -it thegeeklinux bash
4) To check container list : # docker ps
5) To check container memory and cpu. # docker stats thegeeklinux
6) To copy contant from container to host machine or host machine to container # docker cp ./thegeeklinux.war tgl:/opt/tomcat/current/webapps/
Docker Cli Commands Cheat Sheet Printable
7) To check container related logs : # docker logs -f thegeeklinux
-f It will follow log output
8) To commit container : # docker commit -p -a 'thegeeklinux@gmail.com' -m 'commit message' tgl tgl:2.0
-a Author of the container
-m commit message
-p pause container during commit
9) To export container in compressed file # docker export -o /tmp/dockerexport.tar thegeeklinux
NOTE : export command will not export attached volume.
10) To get container information # docker inspect thegeeklinux
NOTE: it will give info in json format
To get ip addres of container # docker inspect -f {{.NetworkSettings.IPAddress}} thegeeklinux
To get mapped port to host : # docker inspect -f '{{(index (index .NetworkSettings.Ports '22/tcp') 0).HostPort}}' thegeeklinux
11) To Stop container: # docker stop thegeeklinux
12) To start container : # docker start thegeeklinux
13) To get container processes # docker top thegeeklinux
14) To rename the container : # docker rename thegeeklinux tgl
15) To restart container : # docker restart docker-scripts
16) To delete container : # docker rm -vf thegeeklinux
-v delete volume also
-f delete container forcely
This is just a cheat sheet of commands and terminology for Docker and ASP.NET Core; it contains commands that you can find in the original cheat sheet, plus a Dockerfile for ASP.NET Core and a quick guide on how to created one from Visual Studio. Hopefully, both developers that are in the process of getting into the containerize world with Docker and developers that are already in but need a quick recap will find it useful.
Basic terminology
List Of Docker Commands
| Term | Short explanation |
|---|---|
| Docker | Docker is a set of platform as a service products that uses OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. Download Docker for Windows here. |
| Image | An image, or more correct, a Docker container image is a lightweight, standalone, executable package of software that includes everything needed to run an application: code, runtime, system tools, system libraries and settings. |
| Container | A container image becomes a container at runtime when they run on Docker Engine |
| Docker Engine | Docker Engine is a container runtime that runs on various Linux (CentOS, Debian, Fedora, Oracle Linux, RHEL, SUSE, and Ubuntu) and Windows Server operating systems… |
| Docker Hub | Docker Hub is a service provided by Docker for finding and sharing container images with your team. |
| Dockerfile | A Dockerfile is a text document that contains all the commands a user could call on the command line to assemble an image. |
Read more information about Docker Container Images and Docker Containers here.
Basic commands
Follows, a list of basic commands that you will regularly need. Run them using command line from the root of your application – where the Dockerfile should exists.
| Term | Short explanation |
|---|---|
docker pull | Retrieve an image from a registry. If you specify only the repository name, Docker will download the image tagged latest from that repository on Docker Hub. e.g. docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/aspnet:3.1 pulls the 3.1 runtime, where docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/sdk pulls the latest .NET Core SDK. |
docker build | Create a new image by running a Dockerfile. User the -t flag to specify the name of the new image and don’t forget the . (build context for the source files for the COPY command)e.g. docker build -t image.name.for.my.app:v1 . |
docker image list | After pulling an image, view the images in your local registry with the docker image list command. |
docker ps | View active containers. Use the -a flag to view all.e.g. docker ps -a |
docker run | Run an image – it will become a container. Specify the option -p for port mapping (left hand side local port, right hand side port exposed by docker) and -d to run it as a background service.Speficy the --name option to set the name of the container.e.g. docker run -p 8080:80 -d --name container.name image.name.for.my.app |
docker stop | Stop an active container by specifying the container ID. Get that with the docker ps commande.g. docker stop elegant_ramanujan |
docker start | Restart a stopped container. e.g. docker start elegant_ramanujan |
docker container rm | Remove a stopped container. Add the -f flag to force remove a running container (not a graceful shutdown)e.g. docker container rm -f elegant_ramanujan |
docker image rm | Remove an image. There is no force flag here, all containers using this image must be stopped. e.g. docker image rm mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/samples:aspnetapp |
Docker Command Reference
A Dockerfile sample
Living in the root of the application, a Dockerfile is just a plain text file; you can either use the following command to create it in Windows, or anyway you like: copy NUL Dockerfile. The sample below contains everything necessary to build and run an image. Comments above each command attempt to provide a bit of clarity:
Docker Cli Commands Cheat Sheet
A cheat with Microsoft Visual Studio
If it happens to have a Visual Studio around, just right click on your main project, select ‘Add’ and then ‘Docker Support…’:
Docker Cheat Sheet Pdf
.
Docker Cheat Sheet 2020
Usually, for ASP.NET Core, I choose ‘Linux’ as Operating System; at the end it comes cheaper if you want to host it, for example, in Azure.
