Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of barium (atomic number: 56), an isotope of this . The first two groups (columns) of the periodic table represent the 's' orbital group.
- Atomic Number of Barium Barium is a chemical element with atomic number 56 which means there are 56 protons and 56 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Barium is.
- Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of barium-137 (atomic number: 56), an isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 56 protons (red) and 81 neutrons (orange). 56 electrons (white) successively occupy available electron shells (rings).
Atomic Number of Barium Atomic Number of Barium is 56. Chemical symbol for Barium is Ba. Number of protons in Barium is 56.
This means that the s,p,d,f electron configuration for Barium. Barium, complete electron configuration.
Barium. Full electron configuration of barium: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 6s2.
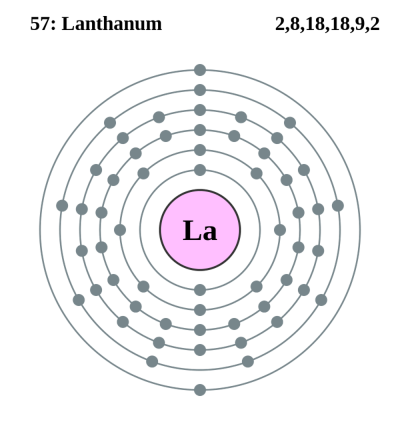
Oxidation States, 2. Electrons Per Shell, 2 8 18 18 8 2.
Molar Mass Of Barium
Electron Configuration, [ Xe] 6s2. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 6s2. Orbital Diagram. Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of barium (atomic number: 56), an isotope of this .Get an answer for 'What is the electron configuration for a Barium ion?
' and find homework help for other Science questions at eNotes. What is the orbital diagram of calcium?
How was it originally determined? Update Cancel. ad by Lucid Software.
Create Easy and Powerful UML Diagrams with Lucidchart. Voted the best UML software for companies, try Lucidchart for free and find out why. What .
Barium can be found in the 6th energy level (row) of the periodic table. It is also in the 2nd group (column) of the periodic table. The first two groups (columns) of the periodic table represent the 's' orbital group.
Atomic Number Of Barium Nitride
This means that the s,p,d,f electron configuration for Barium must end with 6s^2. The 6th row, s .
How to Draw Orbital DiagramsStep by Step: Electron Configurations and Electron Orbital Diagrams Electron Configurations Ex. 1) Mg: 1s 2 2s2 2p6 3s2 ↑↑↑ 1 = 1.
st. layer (row #), s = orbital type, power of 2 = the 2 electrons in the 1s orbital **Move the Helium box next to Hydrogen (above Beryllium.) See the periodic table below.
Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams KEY Draw orbital diagrams for the following elements: 1. phosphorus ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p.Chemistry: The Central Science, Chapter 6, Section 8What is the s,p,d,f configuration of barium?
How to Draw Orbital Diagrams| Socratic
Chemical properties of barium - Health effects of barium - Environmental effects of barium
|
BariumBarium is a silvery-white metal that can be found in the environment, where it exists naturally. It occurs combined with other chemicals, such as sulfur, carbon or oxygen. Ii is very light and its density is half that of iron. Barium oxidizes in air, reacts vigoroulsy with water to form the hydroxide, liberating hydrogen. Barium reacts with almost all the non-metals, forming often poisouning compounds. Applications Barium is often used in barium-nickel alloys for spark-plug electrodes an in vacuum tubes as drying and oxygen-removing agent. It is also used in fluorescent lamps: impure barium sulfide phosphoresces after exposure to the light. Barium in the environment Barium is surprisingly abundant in the Earth's crust, being the 14th most abundant element. High amounts of barium may only be found in soils and in food, such as nuts, seaweed, fish and certain plants. The chief mined ores are barite, which is also the most common and witserite. The main mining areas are UK, Italy, Czech Republic, USA and Germany. Each year about 6 million tonnes are produced and reserves are expected to exceed 400 million tonnes. Health effects of barium
Environmental effects of barium
Back to periodic chart. |
More from 'Elements'


What Is The Atomic Number Of Zirconium
Lenntech (European Head Office)
Distributieweg 3
2645 EG Delfgauw
The Netherlands
Phone: +31 152 610 900
fax: +31 152 616 289
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech USA LLC (Americas)
5975 Sunset Drive
South Miami, FL 33143
USA
Phone: +1 877 453 8095
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech DMCC (Middle East)
Level 5 - OFFICE #8-One JLT Tower
Jumeirah Lake Towers
Dubai - U.A.E.
Phone: +971 4 429 5853
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Copyright © 1998-2021 Lenntech B.V. All rights reserved
