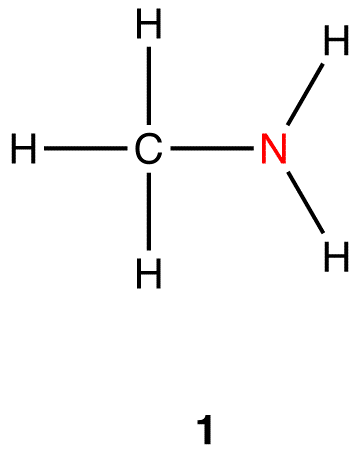
Heteroatom-doped carbon dots (CDs), due to their excellent photoluminescence (PL) properties, attracted widespread attention recently and demonstrated immense promise for diverse applications, particularly for biological applications. The objective of this feature article is to provide a comprehensive overvi JMC B Editor’s choice web collection: ‘‘seeing the unseen updated: advances. Heteroatom is any atom structure that does not have hydrogen or carbon. The molecular structure of a Heteroatom misses carbon or hydrogen and is made of other non-carbon atoms. Examples are oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur and others. Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors.The biggest advantage of conductive polymers is their processability, mainly by dispersion.Conductive polymers are generally not thermoplastics, i.e., they are not thermoformable. Nevertheless, the microenvironment of the single Fe atoms needs to be further engineered to optimize the catalytic performance, which is challenging. In this work, we develop a NaCl-template pyrolysis method to fabricate single Fe atom catalysts with atomically dispersed Fe–heteroatom (N, S) bridge sites anchored on carbon nanosheets.
Heteroatom Organic Chemistry

Learn about this topic in these articles:


chemical reactivity
Hybridization Of Heteroatoms
- In chemical compound: Functional groups
…carbon or hydrogen (termed a heteroatom) is bonded to carbon. All heteroatoms have a greater or lesser attraction for electrons than does carbon. Thus, each bond between a carbon and a heteroatom is polar, and the degree of polarity depends on the difference between the electron-attracting properties of the two…
Read More
Heteroatom Definition
heterocyclic compounds
Heteroatomic Molecules
- In heterocyclic compound
…to the noncarbon atoms, or heteroatoms, in the ring. In their general structure, heterocyclic compounds resemble cyclic organic compounds that incorporate only carbon atoms in the rings—for example, cyclopropane (with a three-carbon-atom ring) or benzene (with a six-carbon-atom ring)—but the presence of the heteroatoms gives heterocyclic compounds physical and chemical…
Read More